FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
VAGINAL HEALTH
Boric acid is a white crystal derived from boron and water. It has antibiotic, ant-viral and anti-fungal properties so it works against fungal and bacterial infections.
Boric acid is a major player in our treatment game. Recommended by gynaecologists, it is a clinically proven, research backed treatment for even the most stubborn yeast infections. When used as a vaginal suppository, it begins to work right away to restore and support your normal vaginal pH, and relieve irritating vaginal symptoms.
Boric Acid does the work of an antibiotic and and anti-fungal. Amazing right? It not only works against Candida albicans, it has your back when you are facing Candida glabrata, a strain responsible for resistant yeast infections that don't respond to other treatments. Boric acid is also effective against trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted infection.
There are relatively few safe and effective alternatives to treating vaginal infections on the market, and continuously using antibiotics and anti-fungals is not great for your gut or your health (Google it!). Boric acid takes the guesswork out of treating common vaginal infections because it can be used safely to treat Yeast, BV, pH imbalance, and even vaginal odour. If you're feeling stress from any of the above, that's where we come in.
Yes! Yes! the same Cranberry PAC's that prevent E-coli bacteria from sticking to the lining of the urinary tract also help to reduce bacteria in the body. The acidic nature of Cranberries may help to support vaginal pH as well!
The vagina is a delicate ecosystem that is normally home to a finely tuned balance of good and bad bacteria. If the bad bacteria present in the vagina becomes unbalanced, it can lead to infection such as bacterial vaginosis (BV) or yeast, and inflammation. Stress, diet, scented bath products, menstrual cycles, and even sex can have an effect on the delicate pH balance in your vagina. These culprits can also play a role in causing vaginitis, and can contribute to a whole range of symptoms including discharge, odour, redness, itching, burning, rawness, stinging, irritation and swelling. Moral of the story, maintaining balance is key.
YEAST INFECTIONS
A yeast infection, also known as Candidiasis, is a common fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of the Candida species, usually Candida albicans. It can affect various parts of the body, with vaginal yeast infections and oral yeast infections (thrush) being among the most well-known types.
Common signs of a yeast infection may include itching, burning, redness, and swelling in the affected area. For vaginal yeast infections, abnormal vaginal discharge is often a key symptom. If you suspect you have a yeast infection, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Yeast infections are primarily caused by an imbalance in the body's natural microorganisms, which can be triggered by factors such as antibiotics, a weakened immune system, uncontrolled diabetes, hormonal changes, or a diet high in sugar.
Symptoms of a yeast infection may vary depending on the affected area but can include itching, burning, swelling, redness, and abnormal discharge. Vaginal yeast infections, for example, often present with itching, a thick white discharge, and discomfort.
Anyone can get a yeast infection, but they are more common in women. Factors such as pregnancy, uncontrolled diabetes, weakened immune system, and the use of certain medications (e.g., antibiotics) can increase the risk.
The duration of a yeast infection can vary. In many cases, with proper treatment, it can be resolved within a few days to a week. However, recurrent infections may require longer treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
Yes, hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy, the menstrual cycle, or menopause, can create an environment conducive to yeast overgrowth. The hormonal shifts can affect the balance of microorganisms in the body, increasing the risk of yeast infections.
BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS
A fishy odor in the vagina could be a symptom of bacterial vaginosis (BV), a common vaginal infection. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
BV can affect women of all ages but is more common in those who are sexually active. Factors like douching and a change in sexual partners can increase the risk of BV.
While both yeast infections and BV can cause vaginal discomfort, they are different conditions. Yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of Candida, resulting in itching and a thick discharge. BV is caused by an imbalance in the vaginal bacteria, leading to a fishy odor and thin, grayish-white discharge.
Women can be more prone to BV due to factors like vaginal douching, multiple sexual partners, or hormonal changes. The specific cause can vary, but these factors can disrupt the balance of vaginal bacteria.
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (UTI'S)
A UTI, or urinary tract infection, is an infection that affects any part of the urinary system, including the bladder, urethra, and kidneys. It is usually caused by bacteria and can result in painful and frequent urination.
Common symptoms of a UTI include a strong urge to urinate, a burning sensation when urinating, cloudy or bloody urine, and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Some individuals, particularly women, are prone to UTIs after sexual intercourse. This is often referred to as "honeymoon cystitis." It can happen because sexual activity may introduce bacteria into the urinary tract. Proper hygiene and urinating before and after sex can help reduce the risk.
No, interstitial cystitis (IC) is not the same as a UTI. IC is a chronic condition that causes discomfort or pain in the bladder and pelvic region. It is not caused by infection, while UTIs are infections of the urinary system.
Untreated UTIs can lead to more severe kidney infections and complications. It's essential to seek treatment promptly to avoid these risks.
HORMONE HEALTH
Peri-menopause is the transitional period before menopause when a woman's body begins to prepare for the cessation of menstruation. It is marked by hormonal fluctuations, which can lead to various symptoms such as irregular periods and hot flashes.
Menopause is the stage in a woman's life when menstruation ceases permanently. Hormonal changes can lead to symptoms like hot flashes, mood swings, and bone density loss.
Adaptogens are natural substances, often herbs or roots, that are believed to help the body adapt to stress and maintain balance. They are commonly used in traditional medicine and wellness practices.
Vaginal dryness can be caused by various factors, including hormonal changes (such as menopause), medications, stress, or underlying medical conditions. It can result in discomfort and pain during sexual activity. Consulting a healthcare provider can help determine the cause and appropriate treatment options.
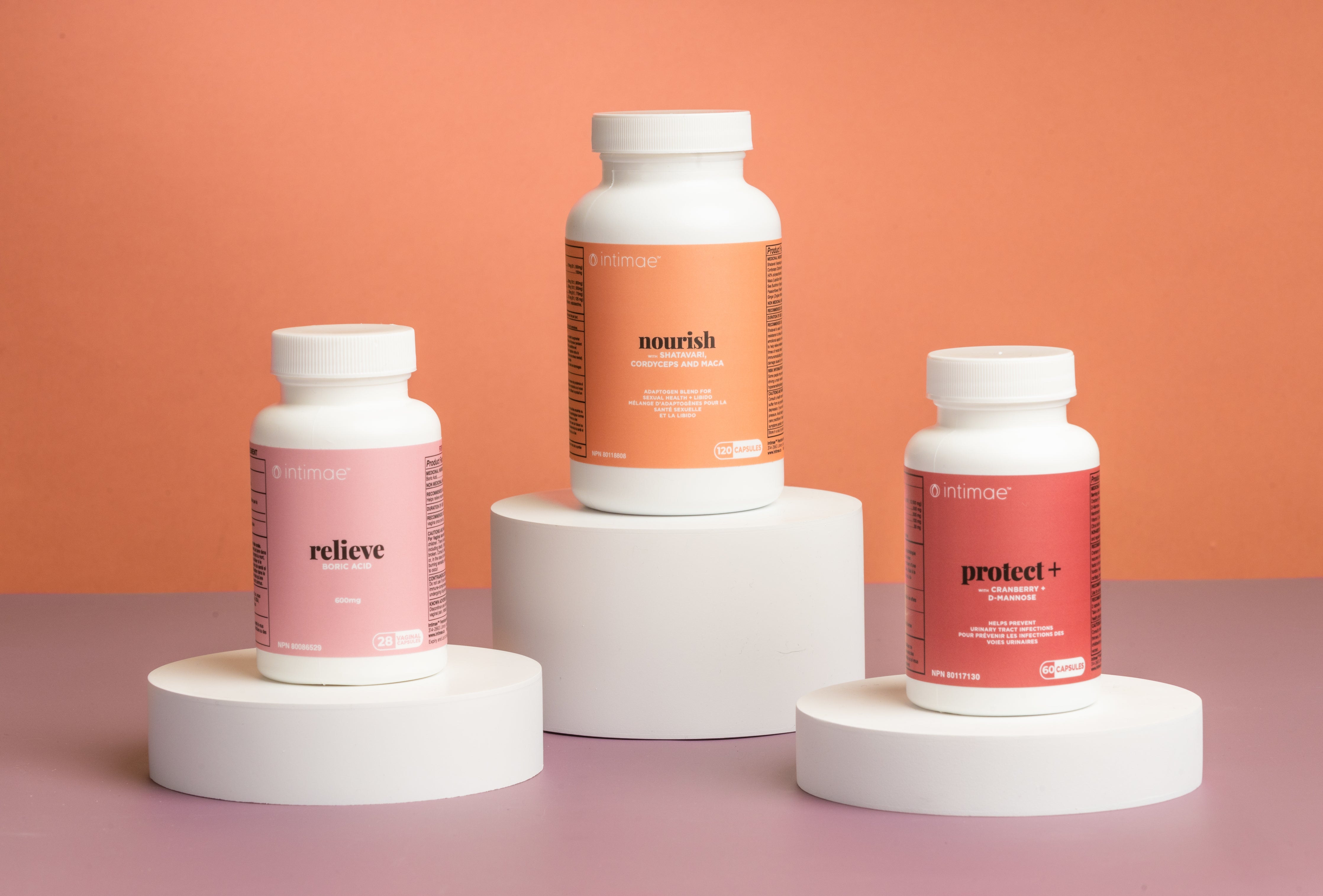
OUR PRODUCTS
No! Using plastic applicators is discouraged for many reasons. Not only can they not be sterilized properly, they can easily scratch the delicate lining of the vagina. You can simply insert the suppositories with a clean finger as high as possible into the vaginal canal.
Nourish is powerful stuff! Our customers usually report seeing an increase in energy first- within the first 1-2 weeks and then an improvement in their libido and sex drive within the first month. Remember, gently nourishing our bodies sexual energy and calming the nervous system is important and everyone is a bit different.
Yes! Absolutely! Using protect as part of a daily vaginal and urinary health maintenance strategy is recommended.
If you're prone to UTIs after sexual activity, it's effective to consider the following preventive measures:
1. Urinate Before and After Sex: This helps flush out potential bacteria that may have entered the urethra during sexual activity.
2. Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps dilute urine and flush out bacteria.
3. Maintain Good Hygiene: Ensure proper cleanliness before and after sex to reduce the risk of introducing harmful bacteria.
4. Avoid Irritants: Use mild, unscented soaps and detergents to avoid irritation in the genital area.
5. Consider Antibiotics: If you frequently experience UTIs after sex, discuss the option of post-coital prophylactic antibiotics with your healthcare provider.